Contribution Margin Ratio Revenue After Variable Costs

Management should also use different variations of the CM formula to analyze departments and product lines on a trending basis like the following. For instance, in Year 0, we use the following formula to arrive at a contribution margin of $60.00 per unit. If contribution margin ratio is equal to the contribution margin is too low, the current price point may need to be reconsidered. In such cases, the price of the product should be adjusted for the offering to be economically viable.
- A low margin typically means that the company, product line, or department isn’t that profitable.
- However, they will play an important part in calculating the net income formula.
- It can also be an invaluable tool for deciding which products may have the highest profitability, particularly when those products use equivalent resources.
- For instance, in Year 0, we use the following formula to arrive at a contribution margin of $60.00 per unit.
- TallyPrime’s security features ensure your data is secure regardless of where you are accessing the data from.
What Is the Contribution Margin Ratio Formula and How Is It Used?
- Instead, management uses this calculation to help improve internal procedures in the production process.
- If the total contribution margin earned in a period exceeds the fixed costs for that period, the business will make a profit.
- Based on the contribution margin formula, there are two ways for a company to increase its contribution margins; They can find ways to increase revenues, or they can reduce their variable costs.
- The ratio is particularly valuable for businesses with multiple product lines, enabling comparative analysis of profitability.
- As such, companies should aim to have the highest contribution margin ratio possible, as this gives them a higher likelihood of covering its fixed costs with the money remaining to reach profitability.
- Striking a balance is essential for keeping investors and customers happy for the long-term success of a business.
Fixed costs are costs that are incurred independent of how much is sold or produced. Buying items such as machinery is a typical example of a fixed cost, specifically a one-time fixed cost. Regardless of how much it is used and how many units are sold, its cost remains the same. However, these fixed costs become a smaller percentage of each unit’s cost unearned revenue as the number of units sold increases.
- This means 40% of each sales dollar is available to cover fixed costs and profits.
- It is considered a managerial ratio because companies rarely report margins to the public.
- The contribution margin represents the revenue that a company gains by selling each additional unit of a product or good.
- To illustrate the concepts of contribution margin, consider the following example.
- Accurate reporting of these costs ensures compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS.
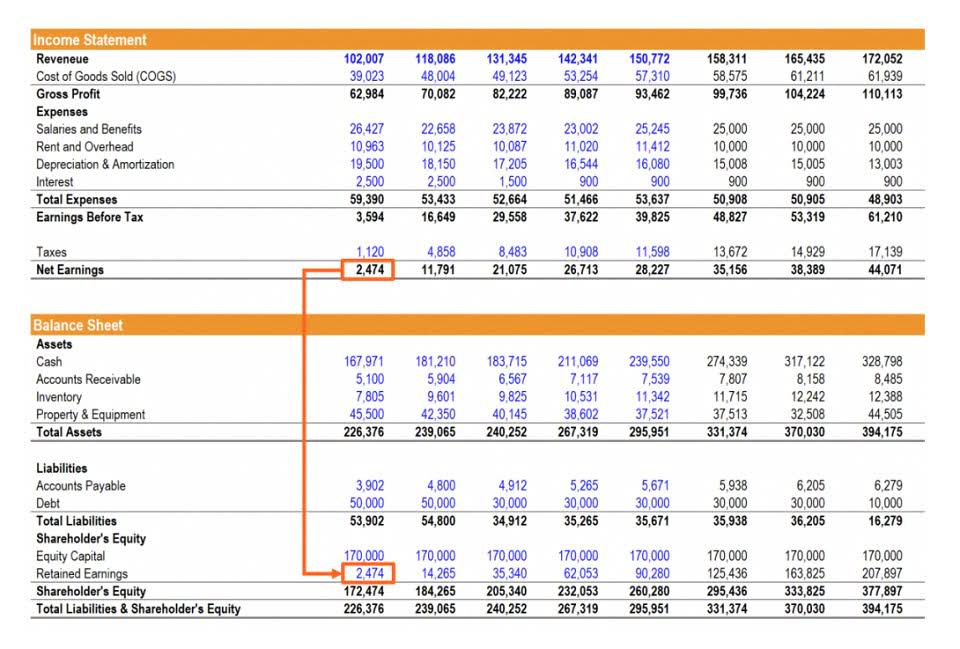
- As of Year 0, the first year of our projections, our hypothetical company has the following financials.
Contribution Margin Calculation Example

Contribution margin income statement, the output of the variable costing is useful in making cost-volume-profit decisions. It is an important input in calculation of breakeven point, i.e. the sales level (in units and/or dollars) at which a company makes zero profit. Breakeven point (in units) equals total fixed costs divided by contribution margin per unit and breakeven point (in dollars) equals total fixed costs divided by contribution margin ratio.
- Understanding financial metrics is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize profitability and make informed decisions.
- As the first step, we’ll begin by listing out the model assumptions for our simple exercise.
- Once you have the two values, revenue and variable costs, you can compute the contribution margin by subtracting the variable costs from revenue.
- The $30.00 represents the earnings remaining after deducting variable costs (and is left over to cover fixed costs and more).
- Selling more units generates greater total contribution margin dollars, which can cover fixed costs and boost profitability.
- Doing this break-even analysis helps FP&A (financial planning & analysis) teams determine the appropriate sale price for a product, the profitability of a product, and the budget allocation for each project.
Contribution margin Formula and analysis
It can be important to perform a breakeven analysis Coffee Shop Accounting to determine how many units need to be sold, and at what price, in order for a company to break even. You need to work out the contribution margin per unit, the increase in profit if there is a one unit increase in sales. Calculate the company’s contribution margin for the period and calculate its breakeven point in both units and dollars. Doing this break-even analysis helps FP&A (financial planning & analysis) teams determine the appropriate sale price for a product, the profitability of a product, and the budget allocation for each project. Should the product be viewed as more of a “loss leader” or a “marketing” expense?

Breakeven Analysis

The companies that operate near peak operating efficiency are far more likely to obtain an economic moat, contributing toward the long-term generation of sustainable profits. As of Year 0, the first year of our projections, our hypothetical company has the following financials. As the first step, we’ll begin by listing out the model assumptions for our simple exercise. Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs. Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates. To find out more about finance careers, try out our interactive Career Map.
